Electrolysis is not a common term in our society; often, hydrogen production or a battery is mentioned in this context. The basic principle of electrolysis is the splitting of a chemical compound under the influence of electricity. For this, at least two electrodes (rods or plates made of various metals) must be immersed in an electrolyte (usually an electrically conductive liquid) and connected to a power source (power supply), after which electrolysis takes place. Based on this principle, hydrogen can be produced.
A battery, however, is a so-called galvanic cell and generates electricity. Charging the battery (accumulator), on the other hand, is an electrolysis process.
The counterpart to electrolysis (where electrical energy is converted into chemical energy) is, for example, the discharging of a battery, where the chemical energy stored in the battery is converted into electrical energy. However, when a battery (accumulator) is recharged, electrolysis occurs again.
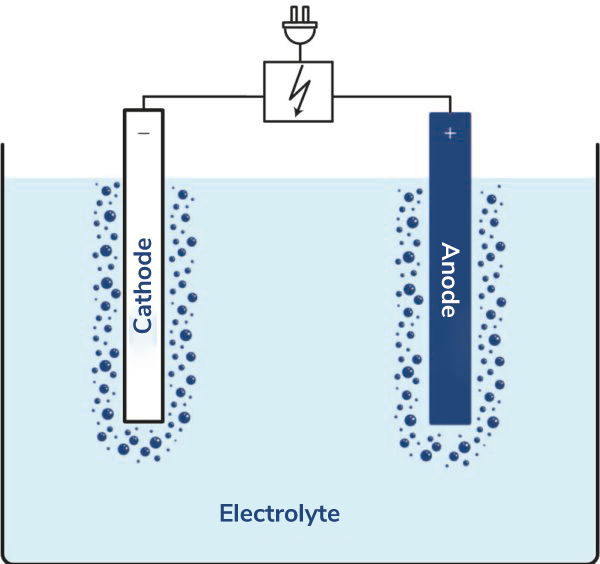
Are there different types of electrolysis?
Electrolysis is an electrochemical process used in many technical applications. An important application is the extraction of substances (metals) such as aluminum or magnesium. In electroplating, electrolysis is used for metal deposition, for example, in nickel or chrome plating of steels. Electrolysis is a common process in technology with many other applications, one of which is water electrolysis.
How does water electrolysis work?
Water (H2O) is a chemical compound made up of hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O). During electrolysis, this compound is broken down by the application of electricity at the electrode surfaces. The oxygen produced in the form of O2 acts as an oxidizer, but not enough to be significant for water treatment/disinfection. The released hydrogen in the form of H2 is of interest, for example, as fuel for hydrogen engines.
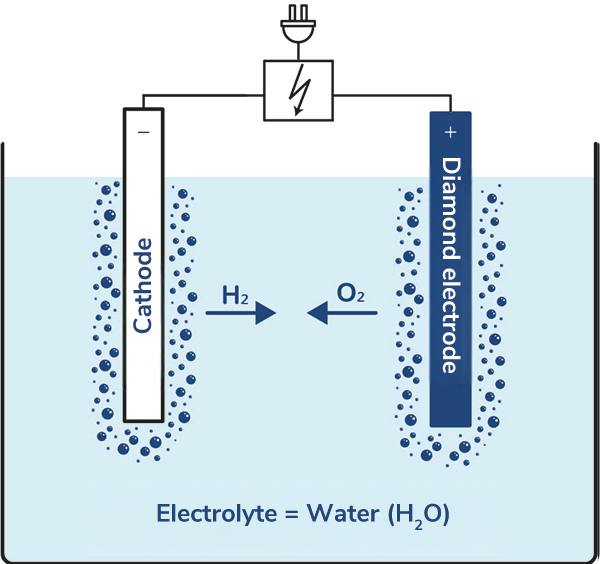
What role do diamond electrodes play in water electrolysis?
pro aqua specializes in water electrolysis using boron-doped diamond electrodes. Most electrodes used for water electrolysis generate oxygen (O₂). The pro aqua diamond electrode plays a special role as it primarily produces oxygen radicals (OH*). Oxygen radicals are highly oxidative and thus very efficient at killing bacteria and breaking down organic contaminants directly in the water. In contrast, the hydrogen (H₂) produced has no significance in wastewater treatment/disinfection. Although hydrogen can burn or explode under certain conditions, it poses no danger to humans or the environment. In pro aqua’s electrolysis process, the hydrogen is safely released into the environment in a controlled manner.
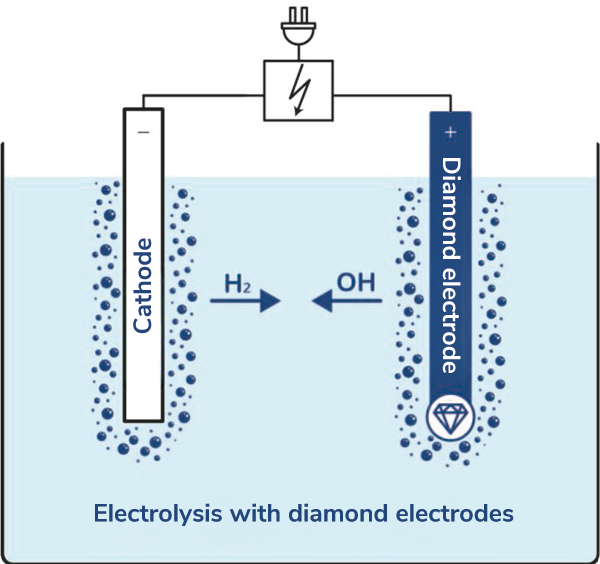
What are the advantages of water electrolysis?
Contaminated water often cannot be used without prior treatment. Commonly known is polluted drinking water that must be cleaned/disinfected before it is suitable for consumption. Beyond drinking water, there are many technical processes in the food industry, medical technology, etc., where water must be free of bacteria and contaminants. Water purification in process engineering is often a combination of mechanical (e.g., filtration) and chemical (e.g., chlorine) methods. In process engineering, water electrolysis is becoming increasingly important to replace chemicals. Electrodes are installed in flow cells where electrolysis takes place. These cells are compact and easy to integrate into process engineering. Except for energy (electricity), electrolysis often requires no additional additives. Organic contaminants present in the water can thus be directly broken down, or bacteria killed, without adding chemicals. This eliminates the need to store and handle often hazardous chemicals for water treatment. Likewise, it removes the transport requirements for chemical delivery, disposal of empty containers, and dependency on suppliers.


